A coronary angiogram is sometimes also known as an angiogram, coronary angiography, cardiac catheterisation or even just as an “angio”.
Heart disease is the leading cause of death in Australia, despite ongoing improvements in prevention, education and treatment. According to the National Heart Foundation, about 3% of Australians have had coronary heart disease at some stage.
If you’ve had a heart attack, angina or unexplained chest pain, you might be referred by your GP to a cardiologist to be assessed for a coronary angiogram.
We’ve prepared this complete guide to coronary angiograms, which explains what it is, why it’s needed and what happens before, during and after the procedure. If you need any further information, please discuss this with your GP or cardiologist.
What is a coronary angiogram and why is it needed?
A coronary angiogram is a common procedure that involves taking X-ray images of the blood vessels leading to the heart. It will give your doctor a clear picture of your heart and its surrounding arteries, helping to diagnose any heart condition and determine what treatment is needed.
The coronary arteries surround the heart and supply the heart muscle with vital blood to keep it pumping. If fatty plaque builds up and clogs your arteries, it can restrict blood flow to the heart. Poor blood flow can cause potentially life-threatening problems such angina, heart attack or heart failure.
A coronary angiogram helps to identify any narrowing or blockages in the arteries leading to the heart, and shows your doctor whether blood flow is being restricted. It will also show exactly which arteries are narrowed, and how severe the blockages are.
“If you have narrowing of any coronary arteries or any symptoms of heart disease, your doctor may recommend that you have a coronary angiogram. It’s a very common procedure that’s used to diagnose the extent of any blockages and how best to manage it,” according to Professor Nigel Jepson, Eastern Heart Clinic’s Medical Director.
“A buildup of plaque can narrow the coronary arteries, slowing down blood flow that’s vital for the heart to function properly. It’s important to diagnose coronary heart disease as quickly as possible, as undiagnosed coronary artery disease can put you at risk of having a heart attack,” he said.
What are the potential risks of having a coronary angiogram?
An angiogram is a common procedure that’s performed regularly at Eastern Heart Clinic.
Risks of complications are low, but every case is different, so relative risks of the procedure are always discussed with individuals by their attending doctor beforehand.
The most common side effect of the procedure is some bruising and/or swelling at the site where the catheter is inserted.
Like all surgical procedures, coronary angiograms do carry some risk, however the overall risk of complications is low. Potential risks – which are generally uncommon – include:
- an allergic reaction to the X-ray dye
- infection
- bleeding
- pain
- abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias)
- heart attack
- stroke
- damage to the kidneys
- damage to the arteries
Professor Jepson said if individuals had particular questions or concerns about the procedure, then it was important they raised those with their doctor beforehand.
What happens before your procedure
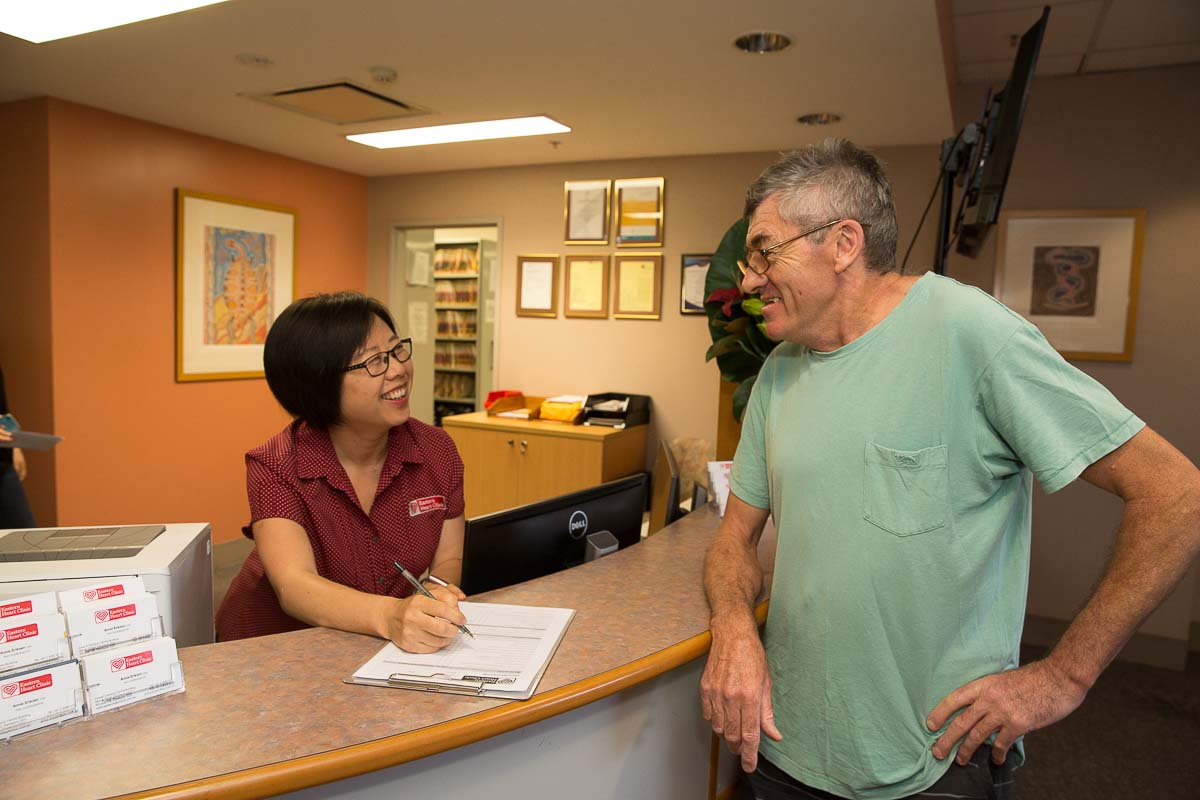

Before you book in to have your coronary angiogram at Eastern Heart Clinic, your doctor will explain what happens during the procedure and answer any questions you might have. You’ll then need to sign a consent form.
If you’re taking certain medications such as Warfarin, Lasix or insulin, your doctor will advise you if you need to stop or change any medications. Warfarin, for instance, may need to be stopped three days before an angiogram. You may also need to take a different type of anticoagulant (blood thinner).
“It’s important to keep taking your medication as normal until you’ve discussed it with your doctor,” Prof Jepson said.
“Your doctor will also let you know if and when to stop taking any medication, and when you can start it again after the procedure.”
The nursing staff will also provide you with additional information about medications before your admission.
If you have any questions about your medication, it’s important to discuss these with your doctor.
Fasting before your procedure
You’ll be required to fast before your coronary angiogram procedure. The details of your fasting will be determined by the time of your procedure. But as a general rule, you’lll be asked to stop eating solid food six hours before your admission. You can have clear fluids at that time, but no cloudy or milky drinks.
You’ll then be asked to stop drinking fluids two hours before admission. That means you can’t have any clear fluids past that time, including water.
These are the general fasting guidelines we use at Eastern Heart Clinic. No matter where you’re having your coronary angiogram procedure, you’ll be given instructions specific to your doctor and clinic prior to admission. If you have any questions, please contact your angiogram clinic beforehand.
How long the procedure takes and what to bring on the day
Patients attending Eastern Heart Clinic for a coronary angiogram can generally expect to be at the clinic for about eight hours in total, from the time of your arrival to the time of your departure.
We recommend you pack a small bag with a few essentials, including:
- your current medications
- any pathology, blood results and X-rays
- referral letters
- your health insurance details
- Medicare card and Veterans Affairs details (if applicable)
- worker’s compensation details (if applicable)
- something to pass the time while you wait, such as reading material, knitting or crosswords along with your reading glasses
- and a few toiletries
What happens during a coronary angiogram
When you arrive for your procedure you will be greeted by our friendly admin and nursing staff, and be asked to change into a hospital gown.
In the pre-operative area, an experienced nurse will go through your medical history and perform some basic observations. A “drip” for intravenous therapy will be inserted as you are likely to receive fluids before the procedure and sedation during the procedure.
You will then be taken into a cardiac catheter laboratory, which looks like an operating room.
You will be awake and lying down on a narrow table for your procedure, and be cared for by doctors and nurses. Usually three or four people will be in the room to look after you.
Usually, some intravenous sedation is given to make you really comfortable and a bit “dozy” but you will not be given a full anaesthetic.
A small amount of local anaesthetic at the site where the catheter (a thin, flexible hollow tube) will be inserted is then used. Note that in the majority of cases, an angiogram causes very little, if any, pain or distress so if you are uncomfortable, you must tell the doctor.
During the procedure, a short plastic tube with a valve is inserted into an artery in your wrist or groin. Your doctor will choose the site that’s best for you.
Catheters are then guided through this insertion site over a wire into your heart and coronary arteries using X-ray.
A liquid iodine based contrast agent (X-ray dye) is then injected through the catheter to visualise the arteries. Usually you will not feel anything when that occurs.
During the angiogram, the valves on the left side of the heart and the pumping chamber may also be checked for any abnormalities. If a picture is taken of the main pumping chamber, you may feel a warm sensation lasting 10 seconds.
At the end of the procedure, the catheter is removed, and pressure is applied to the site where it was inserted. If the procedure was performed via the groin, a “closure device” (stitch or plug) may be inserted.
The procedure normally takes about 30 minutes.
You will then be taken through to our recovery room, where you’ll be monitored and cared for by our experienced recovery room nursing staff.
After your angiogram
Depending on where the catheter was inserted, you may need to lie still for two to six hours in recovery to make sure the wound is sealed and to minimise any bleeding.
Where possible, your doctor will generally visit you in recovery and update you on the procedure and its findings.
Once you’re feeling well recovered, you may be moved into a supervised area of the recovery room where you can sit in a comfortable chair and have something light to eat and drink.
Once you’re ready to leave, the intravenous needle will be removed and you can get dressed.
You won’t be able to drive home, so make sure you’ve arranged for someone to collect you and take you home. If you live alone, we recommend having someone stay with you for the first night after your coronary angiogram, just in case you need some help or support.
Recovering at home
Once you’re at home, keep the bandage on and avoid showering for 24 hours. You can use an ice pack on the puncture site to reduce pain and swelling if needed.
Your doctor will let you know when you can start taking your medication again, such as blood thinners.
Don’t do any strenuous exercise for a few days after the procedure, and avoid taking a bath for one week.
Drink lots of fluids (such as water) to help flush out the dye, and eat a healthy diet with lots of vegetables, fruit and whole grains.
Contact your angiogram clinic straight away if you experience:
- any chest pain or tightness
- fever
- swelling or bleeding where the catheter was inserted
- weakness of numbness in the limb where the catheter was inserted
Call an ambulance immediately if you experience:
- significant bleeding or swelling of the wound
- chest pain or tightness that increases or is severe
If you have any general questions or concerns about your recovery when you’re at home, you should contact your doctor’s rooms or ring your angiogram clinic for advice.
About Eastern Heart Clinic
Eastern Heart Clinic is a private interventional cardiology hospital co-located at the Prince of Wales Hospital at Randwick in Sydney’s eastern suburbs.
One of the largest interventional cardiology hospitals in New South Wales, Eastern Heart Clinic provides diagnostic and interventional cardiology services to public and private patients in metropolitan Sydney and New South Wales.
Learn more about our clinic, cardiology procedures, and what to expect if you’ll be visiting us for a procedure.
Read more:
What is an angiogram?
Day of the procedure
Before your visit
After your visit
Patient privacy and rights


Recent Comments